Measuring functions
The Digital Multimeter offers the following measuring functions:
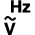 Measurement of alternating voltage
Measurement of alternating voltage 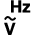 Measurement of the frequency of alternating voltage
Measurement of the frequency of alternating voltage Measurement of direct voltage
Measurement of direct voltage  Measurement of alternating or direct voltage in the millivolt range
Measurement of alternating or direct voltage in the millivolt range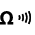 Measurement of resistance
Measurement of resistance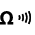 Continuity testing
Continuity testing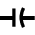 Measurement of the capacitance
Measurement of the capacitance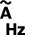 Measurement of alternating current
Measurement of alternating current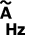 Measurement of the frequency of alternating current
Measurement of the frequency of alternating current Measurement of direct current
Measurement of direct current
The bar graph display (j) resembles the needle of an analogue multimeter. As the bar graph display reacts faster than the digital display, it is suitable for setting peak points and zero points.
The bar graph display is deactivated during measurement of the capacitance. For frequency measurements, the bar graph display and measuring range display show the underlying voltage or current up to 1 kHz.
The number of segments indicates the measured value and is relative to the full scale value of the selected measuring range, which is displayed on the right-hand side of the bar graph display.
- Use for measurements always the proper input terminals, switch position and measuring range.
- Check the test leads for continuity before use. Do not use if the readings are high or noisy.
- Keep your fingers behind the finger guards while using the test leads.
- Turn the rotation switch (2) to the position in the figure.
- Press the Sel button when it is shown in the figure.
- Connect test leads (7) and (8) as shown in the figure.
- Contact the test points with the test probes.
- The measured value is shown on the display (1).
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
Frequency measurement is only carried out with alternating voltage. Use the manual range selection (Range button) to select lower and lower ranges in order to achieve a stable measurement.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
- If necessary, use the manual range selection (Range button) to select a suitable measuring range.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
- If the continuity test is successful, a continuous tone is output.
- Perform a measurement of the direct voltage to confirm whether the capacitor is discharged.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
- Do not take any measurements if the open-circuit potential to earth is more than 600 V.
- Check the fuse of the Digital Multimeter before measuring see Checking the Fuse .
- If the rotation switch is turned to position A or from position A, an audio signal will sound and LEAD will appear on the display. Then check whether the test leads are connected to the right sockets.
- Disconnect the power supply in the circuit to be measured.
- Interrupt the circuit and insert the test leads/test probes in series.
- Switch the power supply back on.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
Frequency measurement is only carried out with alternating current. Use the manual range selection (Range button) to select lower and lower ranges in order to achieve a stable measurement.
- Disconnect the power supply in the circuit to be measured.
- Interrupt the circuit and insert the test leads/test probes in series.
- Switch the power supply back on.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.
- Do not take any measurements if the open-circuit potential to earth is more than 600 V.
- Check the fuse of the Digital Multimeter before measuring see Checking the Fuse .
- Disconnect the power supply in the circuit to be measured.
- Interrupt the circuit and insert the test leads/test probes in series.
- Switch the power supply back on.
- Take the measurement via see Measuring Process.